Plasmon-induced oxidative stress and macromolecular damage in pathogenic bacteria†
Abstract
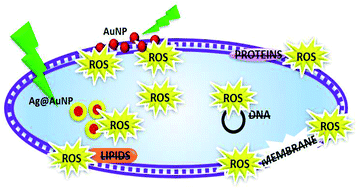
The inactivation mechanism of bacterial growth by Photodynamic Antibacterial Chemotherapy (PACT) employing gold nanoparticles and gold core/silver shell aspartame stabilized bimetallic nanoparticles was studied. Reactive oxygen species were detected and quantified, using fluorescent probes, in the first 4 h of PACT treatment on a reference strain (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213) and two clinical isolates (an extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa). At the same time, damage of essential molecules such as proteins and lipids was found by spectrometric techniques and TEM images analysis. Overall, these results suggest that the oxidative stress caused by the photothermal effect of plasmon excitation leads to irreversible macromolecular damage and therefore to bacterial death. No signals of resistance to PACT with AuNP was found after a total of 31 passages of S. aureus treated with lower doses of the photosensitizer. All this facts support this therapy as a promising antibacterial alternative to antibiotic-resistant microbes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...