MnO2 nanotubes with a water soluble binder as high performance sodium storage materials
Abstract
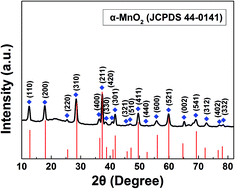
Well dispersed MnO2 nanotubes were synthesized via a hydrothermal method. When tested as anode materials for sodium-ion batteries with sodium polyacrylate (PAANa) as the binder, for the first time, and aluminum as the current collector, the α-MnO2 nanotubes delivered an initial reversible capacity of 357 mA h g−1 and a capacity retention of 358 mA h g−1 after 40 cycles. Moreover, the α-MnO2 nanotubes showed a good rate capability. A capacity of 243 mA h g−1 could be obtained at the rate of 400 mA g−1. The sodium storage mechanism of MnO2 nanotubes and the effects of different binders were also probed through Cyclic Voltammetry (CV), ex situ Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...