Direct surface modification of poly(VDF-co-TrFE) films by surface-initiated ATRP without pretreatment†
Abstract
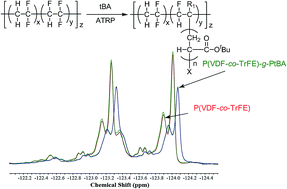
The direct surface modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-trifluoroethylene) (VDF-co-TrFE) copolymer films via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) is presented. The surface-initiated ATRP of tert-butyl acrylate (tBA) and styrene was carried out on poly(VDF-co-TrFE) films containing 75 mol% VDF at 383 K. Such a reaction was monitored by 1H and 19F NMR, attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and by water contact angle measurements. First, the 19F NMR spectra of poly(VDF-co-TrFE)-g-poly(tBA) graft copolymers revealed a reduction in the signal intensity at −123 ppm compared with that of the poly(VDF-co-TrFE) copolymer, indicating that the polymerization of tBA occurred exclusively by fluorine abstraction from the TrFE units. ATR-FTIR spectra of the resulting poly(VDF-co-TrFE)-g-poly(tBA) and poly(VDF-co-TrFE)-g-polystyrene (PS) films evidenced the characteristic absorption frequencies assigned to carbonyl and aromatic C–H stretching. The atomic ratio on the surface of polymer-grafted poly(VDF-co-TrFE) film observed by XPS well agreed with theoretical value of poly(tBA) and PS hompolymers. These results indicated that poly(tBA) and PS were successfully grafted onto the poly(VDF-co-TrFE) film surfaces forming grafting layers, the thickness of which was over 10 nm. The poly(VDF-co-TrFE)-g-poly(tBA) film was subsequently treated with p-toluenesulfonic acid and sodium hydrogen carbonate to modify the grafted chains into poly(acrylic acid sodium salt). Surface-grafted polystyrene was also converted to poly(styrene sulfonic acid sodium salt) by treatment with sulfonic acid. Each reaction step was characterized by ATR-IR and XPS. The static water contact angle of poly(VDF-co-TrFE) copolymer was remarkably reduced from 91 to 15° by hydrolysis of the tBA chains, sulfonation of the styrene chains and their neutralization. A hydrophilic surface was successfully achieved on the poly(VDF-co-TrFE) film by direct surface-initiated polymerization from the outermost surface of the TrFE unit without any change in the bulk physical properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...