Study of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide and benzylideneacetone as electrolyte additives for valve-regulated lead-acid batteries under high-rate partial-state-of-charge conditions
Abstract
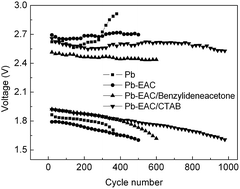
Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide and benzylideneacetone are used as electrolyte additives respectively for inhibiting hydrogen evolution on electrochemically active carbon and prolonging the cycle life of valve-regulated lead-acid batteries working under high-rate partial-state-of-charge conditions. It has been found that the addition of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide or benzylideneacetone in H2SO4 electrolyte can effectively increase the overpotential of hydrogen evolution and decrease the evolution rate of hydrogen on electrochemically active carbon. An appropriate addition amount of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide or benzylideneacetone in the H2SO4 electrolyte of batteries can remarkably slow down the evolution rate of hydrogen on the negative plates, decrease the cut-off charging voltage, and increase the cut-off discharging voltage. Furthermore, the presence of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide or benzylideneacetone prolongs the cycle life of valve-regulated lead-acid batteries under high-rate partial-state-of-charge conditions. In comparison with cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide at the concentration of 240 mg L−1, benzylideneacetone at the concentration of 20 mg L−1 shows better performances in terms of the improved cycle life of the batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...