Sr- and Ni-doping in ZnO nanorods synthesized by a simple wet chemical method as excellent materials for CO and CO2 gas sensing†
Abstract
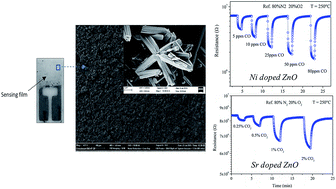
In this study, the effect of Sr- and Ni-doping on the microstructural, morphological and sensing properties of ZnO nanorods has been investigated. Nanorods with different Sr and Ni loadings were prepared using a simple wet chemical method and characterized by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and photoluminescence (PL) analysis. XRD data confirmed that Sr- and Ni-doped samples maintain the wurtzite hexagonal structure of pure ZnO. However, unlike Sr, Ni doping modifies the nanorod morphology, increases the surface area (SA) and decreases the ratio of the IUV/Igreen photoluminescence peak to a greater extent. Sensing tests were performed on thick film resistive planar devices for monitoring CO and CO2, as indicators of indoor air quality. The effect of the operating temperature, nature and loading of the dopant on the sensibility and selectivity of the fabricated sensors towards these two harmful gases was investigated. The gas sensing characteristics of Ni- and Sr-doped ZnO based sensors showed a remarkable enhancement (i.e. the response increased and shifted towards a lower temperature for both gases) compared to the ZnO-based one, demonstrating that these ZnO nanostructures are promising for the fabrication of sensor devices for monitoring indoor air quality.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...