Electrochemical biosensor with graphene oxide nanoparticles and polypyrrole interface for the detection of bilirubin†
Abstract
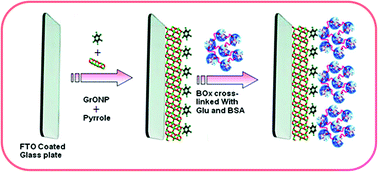
A bilirubin biosensor was fabricated by immobilization of bilirubin oxidase (BOx) on a graphene oxide nanoparticle (GONP) decorated polypyrrole (Ppy) layer electrochemically deposited onto a fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO) glass plate. The enzyme electrode (BOx/GONP@Ppy/FTO), Ag/AgCl as the standard electrode and platinum as the auxiliary electrode were assembled using a potentiostat to develop an amperometric bilirubin biosensor. The characterization of the enzyme electrode was fulfilled using Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and cyclic voltammetry (CV). The biological sensor demonstrated a response at pH 7.5 and 30 °C in only 2 s which was optimum once polarized at +0.2 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The biosensor’s limit of detection (LOD) and required limit of quantification (LOQ) was calculated as 0.1 nM (S/N = 3) and 2.6 nM, respectively. The electrocatalytic reaction illustrated a linear response over the bilirubin/substrate concentration in the range of 0.01 to 500 μM. The half-life of the biosensor is 150 days, during which it could be reused 100 times after keeping the biosensor at 4 °C. The bilirubin levels measured in serum samples of both healthy and jaundice afflicted persons correlated well with the popular colorimetric method, the coefficient of determination (R2) being 0.998.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...