Microsolvation of NO3−: structural exploration and bonding analysis†
Abstract
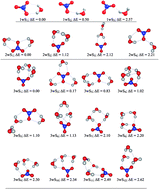
Exploration of the potential energy surfaces (PESs) of various microsolvated species associated with the microsolvation of the nitrate anion using density functional theory methods uncovers a rich and complex structural diversity previously unnoticed in the scientific literature for the [NO3(H2O)n]−, n = 1–6 clusters. Two types of interactions are at play in stabilizing the clusters: traditional water to water and charge assisted nitrate to water hydrogen bonds (HBs). The formal negative charge on oxygen atoms in nitrate strengthens hydrogen bonding among water molecules. There is outstanding agreement between available experimental data (sequential hydration enthalpies, IR spectra, and vertical detachment energies) and the corresponding expectation values obtained from our structures. Each PES is heavily populated in the vicinities of the corresponding global minimum with multiple structures contributing to the experimental properties. The last two statements, in conjunction with results from other works (see for example Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 19241) place a warning on the generalized and naive practice of assigning experimental observations to individual structures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...