Enhancement of oral bioavailability of akebia saponin D by destroying self-micelles and inhibiting multidrug resistance-associated protein mediated efflux
Abstract
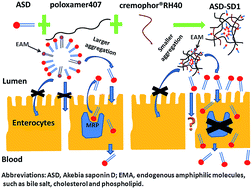
Akebia saponin D (ASD), a triterpenoid saponin with numerous pharmacological activities, is isolated from the rhizome of Dipsacus asper Wall. However, the poor oral bioavailability of ASD restricts its development and clinical use. The purpose of this research is to develop a solid dispersion (ASD-SD) to improve the oral bioavailability of ASD. Poloxamer 407 was employed to prevent ASD from aggregation and Cremophor® RH 40 was used to inhibit multidrug resistance associated protein (MRP) mediated efflux in several new formulations. The particle size was remarkably reduced from 380 nm (ASD) to 230 nm (ASD-SD1 [composition: ASD : Poloxamer 407 : Cremophor® RH 40; ratio: 5 : 9 : 1, w/w/w]). The cumulative release percentage of molecular ASD from dialysis bags was improved from 63.78% (ASD) to 97.12% (ASD-SD1). Single-pass intestinal perfusion studies showed that the absorption of ASD in ASD-SD2 (composition: ASD : Poloxamer 407; ratio: 5 : 9, w/w) was increased approximately 1.8-fold compared to ASD which was mainly due to the particle size reduction, and further promoted by ASD-SD1 about 2.1-fold compared to ASD-SD2 which might be through the MRP inhibition of Cremophor® RH 40. Furthermore, the oral bioavailability in rats was enhanced significantly to 156.9% and 233.1% by ASD-SD2 and ASD-SD1, respectively. Therefore, ASD-SD1 could be a promising drug delivery system to improve the oral absorption of ASD which might be by destroying self-micelles and inhibiting MRP-mediated efflux.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...