The impact of structural variation in simple lanthanide binding peptides†
Abstract
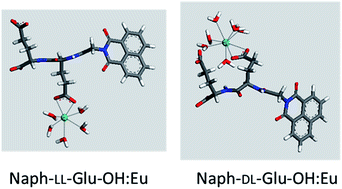
A series of di-, tri- and tetra-peptides were synthesised using L- and D-glutamic acid in order to determine the effects of peptide length and stereochemistry on lanthanide binding affinity. Binding studies with Eu were performed at neutral pH, which is relevant to biological applications, and also under industrially relevant acidic conditions. Increasing peptide length resulted in higher binding affinity but the effect of stereochemistry was dependent on the peptide length. Modelling and experimental characterisation of the peptide : Eu complexes formed suggested that multiple modes of binding were present, with the Eu cation coordinated by the terminal and side chain carboxylic acids of the peptides as well as by backbone carbonyl groups. The peptide with the strongest binding affinity was the tetra-peptide with alternating L- and D-glutamic acid residues, which was able to bind Eu at pH values as low as 4. This peptide was appended with a long-chain alkene and used to covalently functionalise titania nanoparticles. The resulting peptide functionalised titania demonstrated selective sorption of lanthanides over Ca, Ni, Sr and Cs ions. Overall, a deeper understanding of how peptide structure affects lanthanide binding affinity has been gained and the potential of these peptides as selective ligands for separations at acidic pH has been demonstrated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...