Thiaporphyrin-mediated photocatalysis using red light†
Abstract
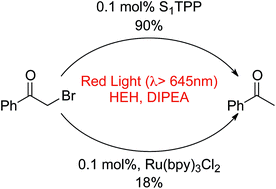
Penetration of light through biological tissue improves in the near-IR windows beyond 650 nm. In an effort to explore the chemical reactivity accessible using this low-energy radiation, this study reveals catalysts and reactions that are experimentally viable with red light. Thiophene-containing porphyrin compounds are capable of catalytic, photo-reductive dehalogenation on an array of α-halo ketone model substrates with low catalyst loadings (0.1 mol%), in the presence of low energy, red light (>645 nm).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...