Abuse tolerance behavior of layered oxide-based Li-ion battery during overcharge and over-discharge†
Abstract
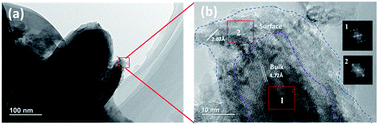
The slight abuse of lithium ion power batteries is inevitable during the practical charge/discharge process. Herein, we investigated the cycle decay behavior of Li(Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3)O2/graphite (NCM/C) high-power battery during slight overcharge (110% SOC) and over-discharge (2 V for lower cut-off voltage). The results show that the cycle life of NCM/C battery is about 1500 cycles at 45 °C, whereas the slight overcharge would markedly accelerate the capacity degradation and shorten the cycle life (only 500 cycles). In contrast, the slight over-discharge causes less damage (about 1300 cycles). A post-mortem study further reveals that the severe aging during overcharge can be mainly ascribed to the capacity loss of the layered oxide cathode material (NCM), followed by an inhomogeneous degradation in the anode. The ex situ XRD results show that the origin of the differing abuse tolerance during overcharge and over-discharge is due to the different crystal structure stability of NCM, which is more unstable in the delithiation state than that in the lithiation state, particularly at an excess delithiation condition corresponding to the overcharge state. Through HR-TEM, it is observed that the NCM suffers from irreversible phase transformation (8–10 nm rock salt phase at surface) even with a slight overcharge. This work provides effective guidance for how to design a voltage control strategy in a battery management system and avoid the capacity decay of NCM/C high-power battery during overcharge and over-discharge application.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...