Synthesis, decoration, and cellular effects of magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
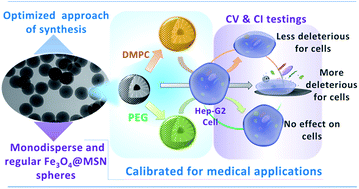
Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSN) are now considered as multifunctional platforms for pharmaceutical development. The goal of this study was to optimize a synthesis procedure to obtain reproducible monodisperse magnetic core@shell Fe3O4@MSN with different coatings and study their uptake by cells. 100 nm core@shell nanoparticles with a unique 18 nm magnetic core were synthesized and covered with PEG groups or coated with a lipid bilayer in a controlled manner and their cellular fate was investigated. Both PEG and lipidic coated nanoparticles exhibit a low toxicity when incubated with Hep-G2 cells compared to pristine ones. Furthermore, the different real-time impedance cellular profiles that were observed and the particles uptake by the cells investigated by TEM suggest different internalization mechanisms or uptake kinetics depending on MSN coverage. This study is a first essential step to ensuring the preparation of well-defined nanomaterials for medical applications; it is considered as a crucial step to be able to perform detailed research about cellular trafficking and signaling pathways.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...