Development of an integrated system for the treatment of rural domestic wastewater: emphasis on nutrient removal
Abstract
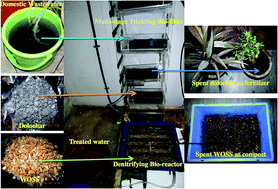
With the aim of enhancing the nutrient removal from rural domestic wastewater while reducing the cost of the treatment process, a novel, integrated treatment system consisting of a multi-stage bio-filter with drop aeration and a post positioned attached growth carbonaceous denitrifying bio-reactor was designed and developed in this study. The bio-filter was packed with ‘dolochar’, a sponge iron industry waste, as an adsorbent mainly for phosphate removal through a physicochemical approach. The denitrifying bio-reactor was packed with many waste organic solid substances (WOSS) as carbon sources and substrates for biomass attachment, mainly to remove nitrate in the biological denitrification process. The performance of the modular system, treating real domestic wastewater was monitored for a period of about 60 days and the average removal efficiencies during the period were as follows: phosphate, 99.48%; nitrate, 92.44%, ammonia, 96.64%, with mean final effluent concentration of 0.153, 5.5, and 1.06 mg L−1, respectively. This treatment system would allow multipurpose reuse of the final effluent. Moreover, the saturated dolochar can be used as a nutrient supply in agricultural practices and the partially degraded carbonaceous substances can also be used as an organic fertilizer after composting. Thus, the system displays immense potential for treating domestic wastewater significantly by decreasing the concentrations of nutrient and most importantly, facilitating the conversion of the waste materials into usable ones.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...