Metal chalcogenide quantum dots: biotechnological synthesis and applications
Abstract
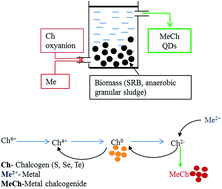
Metal chalcogenide (metal sulfide, selenide and telluride) quantum dots (QDs) have attracted considerable attention due to their quantum confinement and size-dependent photoemission characteristics. QDs are one of the earliest products of nanotechnology that were commercialized for tracking macromolecules and imaging cells in life sciences. An array of physical, chemical and biological methods have been developed to synthesize different QDs. Biological production of QDs follow green chemistry principles, thereby use of hazardous chemicals, high temperature, high pressure and production of by-products is either minimized or completely avoided. In the past decade, significant progress has been made wherein a diverse range of living organisms, i.e. viruses, bacteria, fungi, microalgae, plants and animals have been explored for synthesis of all three types of metal chalcogenide QDs. However, better understanding of the biological mechanisms that mediate the synthesis of metal chalcogenides and control the growth of QDs is needed for improving their yield and properties as well as addressing issues that arise during scale-up. In this review, we present the current status of the biological synthesis and applications of metal chalcogenide QDs. Where possible, the role of key biological macromolecules in controlled production of the nanomaterials is highlighted, and also technological bottlenecks limiting widespread implementation are discussed. The future directions for advancing biological metal chalcogenide synthesis are presented.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...