Assembly of composites into a core–shell structure using ultrasonic spray drying and catalytic application in the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate†
Abstract
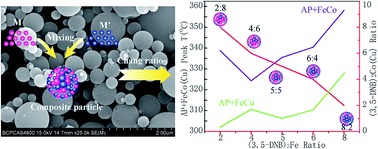
Nano-sized composite combustion catalysts show extensive potential application in the catalytic thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate (AP) because of their synergetic catalytic effect. Facile and effective technology for large-scale preparation of nano-sized composite combustion catalysts is essential for their practical application. Here, a ultrasonic spray drying method is introduced to produce composite micro–nanospheres of 3,5-dinitrobenzoate {(3,5-DNB)M·M′, M = Fe(III), Co(II) or Cu(II)} with a core–shell structure, aimed at providing a facile, large-scale and cost-effective method for manufacturing composite combustion catalysts. The formation mechanism of the core–shell structure is proposed. The results of TEM and SEM illustrate that the heating temperature, carrier gas velocity (pressure), and concentration of the precursor solution have an obvious impact on the droplet-to-particle process. The DSC data indicate that (3,5-DNB)FeCo and (3,5-DNB)FeCu micro–nanospheres are highly effective catalysts for the thermal decomposition of AP, and substantially increase the apparent heat. The (3,5-DNB)FeCo and (3,5-DNB)FeCu micro–nanospheres show good synergetic catalysis which is changed with the component ratio.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...