Variation of electrical properties in thickening Al-doped ZnO films: role of defect chemistry†
Abstract
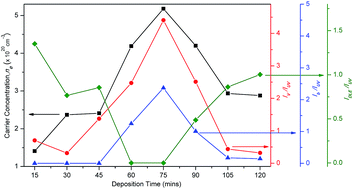
This study addresses the variation in electrical properties in a thickening Al-doped ZnO (AZO) film up to 348 nm and correlates this with its defect chemistry. To this end, AZO films were deposited on soda lime glass substrates at varying deposition times, which ranged from 15 to 120 min at an interval of 15 min, by RF magnetron sputtering. A range of experimental techniques, such as Hall effect measurement, PL measurement, AFM, XPS, XRD, FE-SEM and UV-vis-NIR spectrophotometry, were used to understand the microstructure and optoelectronic properties of the films. It was determined that all the films grew as ZnO hexagonal wurtzite structures with the strong (002) orientation of the crystallites, with an average transmittance of 87–93% in the visible range. However, the electrical properties of these films showed strong dependence on film thickness because of the associated defect chemistry resulting from the film microstructure. A sharp increase in the film carrier concentration is strongly influenced by the presence of shallow donor level defects caused by Zn and extended Zn interstitials, whereas deep donor level defects caused by the occurrence of the oxygen vacancies and excess surface oxygen do not contribute to the carrier generation. The combination of an increased concentration of shallow donor level defects and absence of deep donor level defects correspond with the best values of carrier concentration and carrier mobility leading to the lowest electrical resistivity of 0.913 × 10−3 Ω cm and highest observed film quality at 242 nm thickness, which was obtained at 60 min deposition time. Moreover, this study reveals the necessity of using an appropriately thick AZO film as the TCO. Finally, a narrow PL spectrum, with strong violet and/or blue emissions, is an indication of a high quality TCO. This study also sheds light on the use of PL as an alternate tool to understand the microstructure and electrical properties of a TCO.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...