Facile preparation of hyaluronic acid-modified Fe3O4@Mn3O4 nanocomposites for targeted T1/T2 dual-mode MR imaging of cancer cells†
Abstract
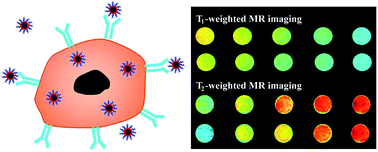
We report a facile approach to synthesizing hyaluronic acid (HA)-modified Fe3O4@Mn3O4 nanocomposites (NCs) for targeted T1/T2 dual-mode magnetic resonance (MR) imaging of cancer cells. In this work, branched polyethyleneimine (PEI)-coated Fe3O4@Mn3O4 NCs (Fe3O4@Mn3O4-PEI NCs) were first synthesized via a one-pot hydrothermal route, followed by modification of HA on the particle surface via PEI amines. The formed Fe3O4@Mn3O4-PEI-HA NCs were well characterized via different techniques. Our results manifest that the formed Fe3O4@Mn3O4-PEI-HA NCs possess good water dispersibility, colloidal stability, cytocompatibility in the studied concentration range, and targeting specificity to CD44 receptor-overexpressing cancer cells. Due to the coexistence of Fe3O4 and Mn3O4 in the particles, the Fe3O4@Mn3O4-PEI-HA NCs display relatively high r2 (143.26 mM−1 s−1) and r1 (2.15 mM−1 s−1) relaxivities, and can be used as an efficient nanoprobe for targeted T1/T2 dual-mode MR imaging of cancer cells in vitro. The developed Fe3O4@Mn3O4-PEI-HA NCs may hold great promise to be used as a nanoplatform for theranostics of different biological systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...