Docetaxel-loaded SiO2@Au@GO core–shell nanoparticles for chemo-photothermal therapy of cancer cells†
Abstract
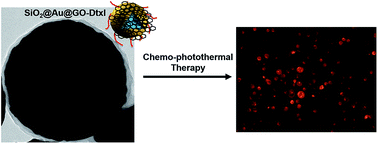
The multifunctional antitumor SiO2@Au@GO core–shell nanoparticles (NPs) have been fabricated for serving as drug nanocarrier and photothermal inducer. The core–shell NPs exhibited high loading capacity of docetaxel (Dtxl) and pH-dependent drug release property as well as low cytotoxicity (concentration < 0.2 mg mL−1). Compared with chemotherapy alone, human prostate cancer cell incubated with Dtxl-loaded SiO2@Au@GO NPs in vitro were found to have undergone morbidity on exposure to near-infrared (NIR) light (780 nm, 5 W cm−2). It is expected that the multifunctional nanoparticles with unique core–shell structure will lead to new opportunities in nanomedicine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...