Design and development of an in situ synthesized layered double hydroxide structure of Fe-induced hydroxyapatite for drug carriers
Abstract
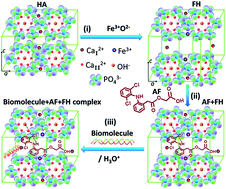
Iron (Fe)-induced hydroxyapatite (HA) layered double hydroxides (LDH) with different concentrations of Fe (FH95 and FH85) were prepared by a novel in situ coprecipitation method. For the first time, LDH is intercalated with calcium cations (CaI2+) by producing Frenkel defects. The LDH structure was precisely characterized by thermogravimetric analysis and X-ray diffraction study. The exfoliation in the basal planes was also confirmed by high resolution transmission electron microscopy. Hydrophilicity and change in mass in vitro swelling in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) medium were characterized to check the wettability of the pellet samples in aqueous media. The morphological and elemental study of the carriers was done before and after aceclofenac (AF) drug loading by a field emission electron microscope. Interactions of AF with LDH drug carriers (FH85 and FH95) were studied by Fourier transforms infrared spectroscopy. The AF drug-release mechanism of these novel LDH carriers was diffusion. The AF drug loading efficiency and releasing criteria were found to be better in FH95 than the carrier FH85. The FH95 LDH carrier can store the AF drug and can release the drug in a controlled manner in aqueous medium of PBS under simulated body conditions. Furthermore, the newly developed LDH material is highly biocompatible as well as a potential drug carrier. Therefore, the developed LDH drug carrier could be a potential drug scavenger for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as AF.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...