Efficient removal of cationic dyes using a new magnetic nanocomposite based on starch-g-poly(vinylalcohol) and functionalized with sulfate groups†
Abstract
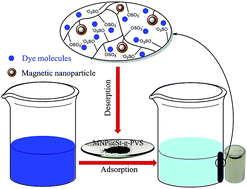
A magnetic nanoparticle@starch-g-poly(vinyl sulfate) nanocomposite (MNP@St-g-PVS) as a new magnetic nano-adsorbent has been prepared based on graft copolymerization of vinyl acetate onto starch in the presence of magnetic nanoparticles, where the acetate groups were converted to hydroxyl groups followed by the sulfation of the hydroxyl groups using chlorosulfonic acid. Characterization of this magnetic nanocomposite was carried out by FTIR, TGA, XRD, VSM, SEM, TEM and elemental analysis. The resulting nanocomposite was used as an adsorbent for the removal of typical cationic dyes, methylene blue (MB) and malachite green (MG), from aqueous solutions. All experimental parameters that can affect the adsorption behavior, including the pH of the dye solution, initial dye concentration, contact time and temperature were investigated. Furthermore, study of the kinetics and isotherm adsorption indicated that the adsorption process is well fitted by pseudo-second-order kinetic and Langmuir isotherm models, respectively. The MNP@St-g-PVS magnetic nano-adsorbent showed remarkable adsorption capacities in the removal of cationic dyes (621 mg g−1 for MB and 567 mg g−1 for MG), compared to most of the other adsorbents. It is worth noting that the prepared adsorbent has a robust structure and could be recovered without a significant loss of adsorption ability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...