Antimicrobial electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds for gingival fibroblast growth
Abstract
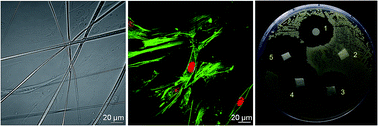
This study discusses the value of polymer electrospun materials in three-dimensional (3D) scaffolds and antibacterial wound dressings for potential dental applications. Polycaprolactone (PCL) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) nanofibers were used as bases for gingival fibroblast (HGF-1 cell line) growth. HGF-1 cells cultured on both types of nanofibers were found to have normal morphology and growth by selective staining of the nuclei and cytoskeleton. The nanofibers were synthesized on different collectors to obtain a random or parallel alignment. Cell growth was observed along the nanofibers. In addition, antibiotics were incorporated within the nanofibers and studied by means of Raman spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. The release profile of the antibiotics was determined by broad band dielectric measurements. The drug was found to be released by Fickian diffusion. The WST-1 test found PCL and PCL/ampicillin nanofibers to have minimal cytotoxicity. The antibacterial activity of materials containing ampicillin was evaluated by zone inhibition against a selected oral strain of Streptococcus sanguinis. The bacterial growth was inhibited by antibiotic release from PCL/ampicillin mats.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...