Hydrophobic myristic acid modified PAMAM dendrimers augment the delivery of tamoxifen to breast cancer cells†
Abstract
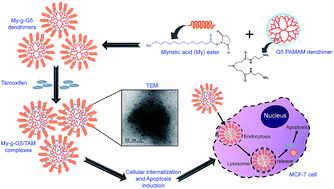
In the present study, cationic generation 5 polyamido amine (G5 PAMAM) dendrimers were hydrophobically modified by grafting the surface with lipid-like myristic acid (My) tails to augment their potential as a drug delivery vector in vitro. Nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) measurements confirmed the presence of myristic acid tails at the dendrimer periphery (My-g-G5). Tamoxifen (TAM) an estrogen agonist, was entrapped in the My-g-G5 domains to impart them with anticancer properties. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observations indicate these My-g-G5/TAM complexes to be around 6–8 nm in size. Further, in vitro drug release studies ascertained the ability of My-g-G5/TAM complexes to release TAM in a sustained fashion under acidic conditions (pH 5.5). Cellular uptake studies revealed lysosomes as the target organelles of these nanocomplexes. MTT assay suggested good cell viability of My-g-G5 dendrimers and strong inhibitory effects of My-g-G5/TAM complexes in MCF-7 (human breast adenocarcinoma, estrogen receptor (ER) positive) cells. Dual fluorescence staining, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, cell cycle analysis, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), change in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP, ΔΨ) and gene expression studies revealed the apoptosis-inducing ability of My-g-G5/TAM in MCF-7 cells. Based on our findings, we present these hydrophobically modified G5 PAMAM dendrimers as prospective nanocarriers for TAM delivery for anticancer applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...