Fabrication and surface stochastic analysis of enhanced photoelectrochemical activity of a tuneable MoS2–CdS thin film heterojunction†
Abstract
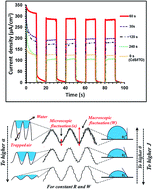
A very simple and well-controlled procedure was employed to prepare CdS nanoparticle/few-layer MoS2 nanosheet/Indium tin oxide (ITO) thin film heterostructures. To tune and fabricate the CdS/MoS2(t)/ITO thin films with various surface topographies, first electrophoretic deposition (EPD) was used to deposit MoS2 nanosheets on the ITO substrate under an optimized applied potential difference (8 V) for different deposition times (t) of 30, 60, 120 and 240 s. Then, CdS nanoparticles were deposited via a successive ion layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) technique. The highest photo-current density of 285 μA cm−2 was measured for the CdS/MoS2(60 s)/ITO sample, which was about 2.3 times higher than the value obtained for bare CdS/ITO. The photo-enhancement mechanism of the CdS/MoS2(t)/ITO heterostructures was described using a stochastic model. The results show that the CdS/MoS2(60 s)/ITO electrode exhibits the highest roughness exponent (2α = 0.67) with the smoothest nanometric fluctuations, resulting in the best wetting properties, and thus, the highest interaction between the electrolyte and the sample surface, leading to the highest PEC activity. On the other hand, the samples with small α possess rough and nanometric-jagged fluctuations. The air trapping inside these microscopic surface fluctuations reduces the wettability as well as surface interaction between the sample and the electrolyte, resulting in low photo-current density.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...