Remote triggering of thermoresponsive PNIPAM by iron oxide nanoparticles
Abstract
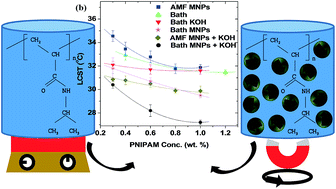
A thorough study on the elements that affect the lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) solutions during alternating magnetic field (AMF) heating, using iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (IO MNPs) is reported. Several PNIPAM solutions with different concentrations of IO MNPs were prepared and characterized using transmission electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, and Raman spectroscopy. While increasing the IO MNP concentration was observed to decrease the specific absorption rate (SAR), the presence of PNIPAM in the solution facilitated the dispersal and disaggregation of IO MNPs leading to a slight improvement in the SAR. In situ transmission measurements were used to determine the LCST of PNIPAM under various aqueous concentrations with dispersed IO MNPs. A systematic decrease in the LCST from 34 °C to 31 °C was observed as the concentration of PNIPAM was increased from 0.3 wt% to 1.0 wt%, while keeping the concentration of IO MNPs constant. On the other hand, varying the ion concentration of the PNIPAM solutions by adding adjusted KOH pellets, showed a pronounced lowering of the LCST by 3–4 °C at all PNIPAM concentrations, which has been shown to be further affected by the presence of the nanoparticles. The remote triggering of volume phase transition in PNIPAM solutions by raising the temperature above the LCST using IO MNPs as reported here is important in targeted drug-delivery applications using thermo-responsive polymers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...