A mechanistic study on guanidine-catalyzed chemical fixation of CO2 with 2-aminobenzonitrile to quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione†
Abstract
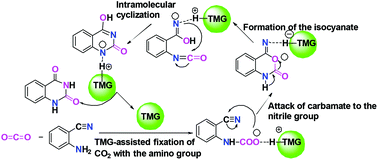
The organic base-catalyzed mechanism of chemical fixation of CO2 with 2-aminobenzonitrile to quinazoline-2,4-(1H,3H)-dione has been studied by means of density functional theory (DFT) calculations on such reactions in the presence of two typical organic guanidines: 1,1,3,3-tetramethylguanidine (TMG) and 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-1-ene (TBD). The calculations reveal that the guanidine-catalyzed reaction prefers to proceed through a general base mechanism rather than the CO2 activation mechanism that involves the formation of guanidine–CO2 adducts. In the general base mechanism, the guanidine primarily plays a catalytic role as a strong base to promote the fixation of CO2 by the amino group of 2-aminobenzonitrile, leading to a carbamate intermediate. Meanwhile, the acidity of guanidinium and the synergistic catalysis from the amino group of 2-aminobenzonitrile are also found to be crucial for lowering energy barriers of intramolecular nucleophilic attack from the carbamate to the nitrile group and the isocyanate intermediate formation via the ring-opening step. In comparison with the TBD-catalyzed reaction, the catalytic advantage of TMG is exerted at the less H-bonding interaction between [TMGH]+ guanidinium and the carbamate anion, owing to its own acyclic framework.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...