Electron-deficient copper pnictides: A2Mg3Cu9Pn7 (A = Sr, Eu; Pn = P, As) and Eu5Mg2.39Cu16.61As12†
Abstract
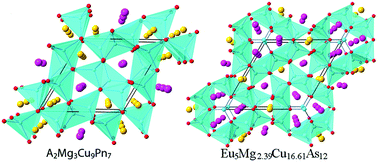
A series of new magnesium copper pnictide intermetallics, A2Mg3Cu9Pn7 (A = Sr, Eu; Pn = P, As) and Eu5Mg2.39Cu16.61As12, were synthesized through high temperature flux reactions. By the single-crystal X-ray diffraction technique, their structures were accurately determined. Sr2Mg3Cu9P7, Eu2Mg3Cu9P7, Sr2Mg3Cu9As7 and Eu2Mg3Cu9As7 crystallize in the Zr2Fe12P7 structure type (S.G. P![[6 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0036_0304.gif) , no. 174) with cell parameters: a = 9.7736(19)/9.7417(7)/10.0550(10) Å/10.0410(8) Å, c = 3.9280(16)/3.9008(5)/4.0544(9)/4.0364(6) Å, respectively, while Eu5Mg2.39Cu16.61As12 adopts the Zr5Co19P12 structure type (S.G. P
, no. 174) with cell parameters: a = 9.7736(19)/9.7417(7)/10.0550(10) Å/10.0410(8) Å, c = 3.9280(16)/3.9008(5)/4.0544(9)/4.0364(6) Å, respectively, while Eu5Mg2.39Cu16.61As12 adopts the Zr5Co19P12 structure type (S.G. P![[6 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0036_0304.gif) 2m, no. 189) with cell parameters of a = 13.2521(6) Å and c = 4.0910(3) Å. These compounds can be viewed as an extensive branch of the ternary RE−M−Pn system (RE = rare-earth elements; M = transition metals; Pn = pnictogen) with the metal-to-nonmetal ratio being close or equal to 2 : 1. Interestingly, with the divalent alkaline-earth cations being introduced, these metal-rich phases exhibit electron deficiency according to the DFT calculations. Eu2Mg3Cu9As7 is metallic based on the resistivity measurement, consistent with theoretical prediction, and the magnetic susceptibility data of Eu2Mg3Cu9As7 confirmed the divalent oxidation state and weak ferromagnetic coupling for the europium cations.
2m, no. 189) with cell parameters of a = 13.2521(6) Å and c = 4.0910(3) Å. These compounds can be viewed as an extensive branch of the ternary RE−M−Pn system (RE = rare-earth elements; M = transition metals; Pn = pnictogen) with the metal-to-nonmetal ratio being close or equal to 2 : 1. Interestingly, with the divalent alkaline-earth cations being introduced, these metal-rich phases exhibit electron deficiency according to the DFT calculations. Eu2Mg3Cu9As7 is metallic based on the resistivity measurement, consistent with theoretical prediction, and the magnetic susceptibility data of Eu2Mg3Cu9As7 confirmed the divalent oxidation state and weak ferromagnetic coupling for the europium cations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...