An asymmetric binuclear zinc(ii) complex with mixed iminodiacetate and phenanthroline ligands: synthesis, characterization, structural conversion and anticancer properties†
Abstract
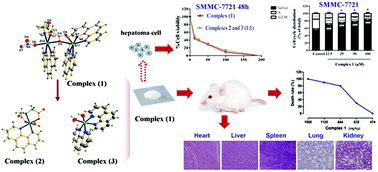
Transition metal complexes with substituted high affinity mixed ligands as potential anticancer agents can overcome the drawbacks of platinum-based drugs that are currently being marketed. Here, a new water-soluble asymmetric binuclear iminodiacetato-zinc(II) complex [Zn2(ida)(phen)3(NO3)]·NO3·5H2O (1) with a phenanthroline ligand has been synthesized and fully characterized with a wide range of analytical techniques including single crystal X-ray diffraction as well as spectroscopic techniques, such as FT-IR, UV/Vis, photoluminescence spectroscopy, and furthermore by elemental and thermogravimetric analyses. Moreover, unprecedented (H2O)10 water clusters consisting of a quasi-planar tetramer and six dangling water molecules were observed in the void space of 3D supramolecular assemblies. The conversion behavior of (1) into two monomeric species [Zn(ida)(phen)(H2O)] (2) and [Zn(phen)2(H2O)2]2+ (3) in aqueous solution was first studied by solid-state/solution NMR, ESI-MS, and solution UV/vis spectra. Next, these zinc(II) complexes (1–3), a mixture of (2) and (3) (mole ratio 1/1), ligands (phen and ida) and zinc ions (ZnCl2 and ZnSO4) were further evaluated for the in vitro cytotoxic profile in human hepatoma cell lines (HepG2 and SMMC-7721). We found that complex (1) effectively inhibited the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells, which is similar to a mixture of (2) and (3) in a 1 : 1 molar ratio, and IC50 values of (1) were almost about 20–50% of (2) or (3). Therefore, this binuclear complex (1) mainly acts as a cooperative inhibitor with complexes (2) and (3) toward tumor growth in solution. We further extended the preliminary research of complex (1) and found that (1) could induce cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase. Additionally, overdosing on (1) exhibited low toxicity of mice (LD50 of (1) in ICR mice = 736 mg kg−1, with 95% confidence interval 635–842 mg kg−1). In conclusion, complex (1) with a high antitumor activity and low toxicity provides a new strategy for the treatment of liver cancer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...