Synthesis of a new cationic non-conjugated polymer for discrimination of microbial pathogens†
Abstract
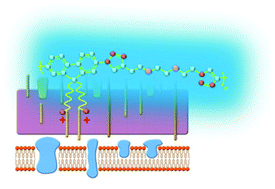
The detection of pathogens plays a crucial role in clinical applications. In recent years, conjugated polymers are favorable in chemical and biological detections due to their remarkable light harvesting and optical signal amplification characteristics. However, most of the conjugated polymers exhibit cytotoxicity due to their rigid and hydrophobic backbone. To circumvent these deficiencies, one promising strategy is to develop a non-conjugated polymer with fluorescence, low-toxic and water-soluble characteristics. In this paper, we describe the synthesis and characterization of a novel water-soluble non-conjugated polymer (P1) containing chromophores with groups of quaternary ammonium cations in the side-chains and non-conjugated linkers of oligo(ethylene glycol) (OEG), the capability of which would not only increase the flexibility and hydrophilicity of the main-chain, but also reduce nonspecific adsorption to proteins and cell surfaces of microbial pathogens. Thus, through the balance between pendent groups of quaternary ammonium cations and OEG linkers, self-luminous P1 molecules could realize visual optical discrimination and detection of three kinds of microbial pathogens rapidly and simply by using a fluorescence microscope.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...