Side-chain-to-tail cyclization of ribosomally derived peptides promoted by aryl and alkyl amino-functionalized unnatural amino acids†
Abstract
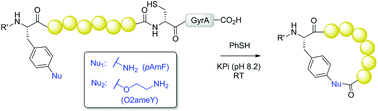
A strategy for the production of side-chain-to-tail cyclic peptides from ribosomally derived polypeptide precursors is reported. Two genetically encodable unnatural amino acids, bearing either an aryl or alkyl amino group, were investigated for their efficiency toward promoting the formation of medium to large-sized peptide macrocycles via intein-mediated side-chain-to-C-terminus cyclization. While only partial cyclization was observed with precursor proteins containing para-amino-phenylalanine, efficient peptide macrocyclization could be achieved using O-2-aminoethyl-tyrosine as the reactive moiety. Conveniently, the latter was generated upon quantitative, post-translational reduction of the azido-containing counterpart, O-2-azidoethyl-tyrosine, directly in E. coli cells. This methodology could be successfully applied for the production of a 12 mer cyclic peptide with enhanced binding affinity for the model target protein streptavidin as compared to the acyclic counterpart (KD: 5.1 μM vs. 22.4 μM), thus demonstrating its utility toward the creation and investigation of novel, functional macrocyclic peptides.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...