Selective recognition of c-MYC G-quadruplex DNA using prolinamide derivatives†
Abstract
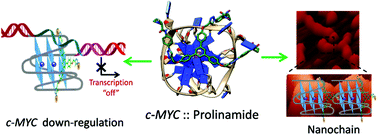
Herein we report the design, synthesis, biophysical and biological evaluation of triazole containing prolinamide derivatives as selective c-MYC G-quadruplex binding ligands. A modular synthetic route has been devised for prolinamide derivatives using a copper(I) catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC). The Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) melting assay indicates that prolinamide trimers can significantly stabilize G-quadruplex structures over duplex DNA compared to prolinamide dimers. The fluorescent intercalator displacement (FID) assay shows that a trimer with prolinamide side chains at the para-position of the benzene ring can discriminate between different quadruplex structures and exhibits the highest binding affinity towards the c-MYC G-quadruplex structure. Molecular modeling studies reveal that the prolinamide trimer stacks upon the terminal G-quartet of the c-MYC G-quadruplex. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) analysis reveals that the tris-prolinamide ligand can be used to regulate the assembly of novel supramolecular nanoarchitectures. Further, in vitro cellular studies with human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells indicate that the tris-prolinamide derivatives can inhibit cell proliferation and reduce c-MYC expression in cancer cells.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Talent

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...