Stationary bubble formation and Marangoni convection induced by CW laser heating of a single gold nanoparticle†
Abstract
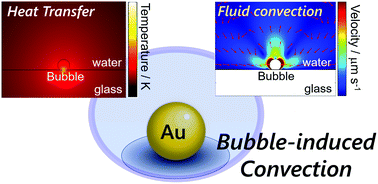
Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) efficiently convert incident light into heat under the resonant conditions of localized surface plasmon. Controlling mass transfer through plasmonic heating of Au NPs has potential applications such as manipulation and fabrication within a small space. Here, we describe the formation of stationary microbubbles and subsequent fluid convection induced by CW laser heating of Au NPs in water. Stationary bubbles of about 1–20 μm in diameter were produced by irradiating individual Au NPs with a CW laser. Spatial profiles and velocity distribution of fluid convection around the microbubbles were visualized by the wide-field fluorescence imaging of tracer nanospheres. To evaluate the bubble-induced convection, numerical simulations were performed on the basis of general heat diffusion and Navier–Stokes equations. A comparison between the experimental and computational results revealed that a temperature derivative of surface tension at the bubble surface is a key factor to control the fluid convection. Temperature differences of a few Kelvin at the bubble surface resulted in convective velocities ranging from 102 to 103 μm s−1. The convective velocity gradually increased with increasing bubble diameter. This article covers both natural and Marangoni convection induced by plasmonic heating of Au NPs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...