In situ formation of nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles on hollow carbon spheres as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts †
Abstract
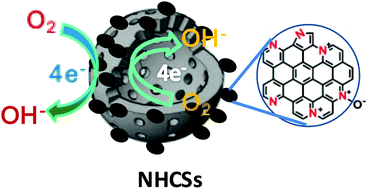
In situ formation of nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles on hollow carbon spheres (NHCSs) were successfully realised via a simple, scalable emulsion polymerization route using melamine as the nitrogen precursor, followed by thermal treatment at 1000 °C in N2. All NHCSs show large BET specific surface areas (648.2–837.7 cm2 g−1) and pore volumes (0.91–1.16 cm3 g−1), evidently superior to N-free hollow carbon spheres (HCSs) (524.3 cm2 g−1 and 0.48 cm3 g−1, respectively). This unique nanocomposite has hierarchical micro-/mesoporosity (1.9 nm and 16.2–19.0 nm). The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements indicate the successful introduction of N atoms into the carbon framework and that the N-doping level can be controlled by changing the amount of melamine. The N-doping by adding melamine during the hydrothermal process not only affects the morphologies and porosities of the final samples, but also improves the electrocatalytic activity compared to N-free HCSs. NHCS-2, prepared with the molar melamine/hexamethylentetramine ratio of 1, showed the best electrocatalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in terms of onset potential, half-wave potential and limit current density. The NHCS-2 exhibited not only excellent activity with a mainly four-electron reaction pathway, but also superior long-term durability and methanol tolerance to that of commercial Pt/C in alkaline solution. The excellent electrocatalytic activity of the NHCS-2 is mainly due to its high relative content of pyridinic- and graphitic-N groups as well as unique hierarchical micro-/mesoporosity and a large specific surface area, advantageous for mass transfer and thus improving the electrocatalytic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...