Spectroscopic metrics allow in situ measurement of mean size and thickness of liquid-exfoliated few-layer graphene nanosheets†
Abstract
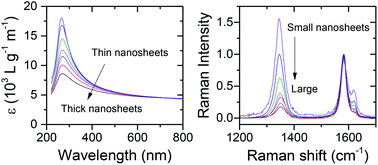
Liquid phase exfoliation is a powerful and scalable technique to produce defect-free mono- and few-layer graphene. However, samples are typically polydisperse and control over size and thickness is challenging. Notably, high throughput techniques to measure size and thickness are lacking. In this work, we have measured the extinction, absorption, scattering and Raman spectra for liquid phase exfoliated graphene nanosheets of various lateral sizes (90 ≤ 〈L〉 ≤ 810 nm) and thicknesses (2.7 ≤ 〈N〉 ≤ 10.4). We found all spectra to show well-defined dependences on nanosheet dimensions. Measurements of extinction and absorption spectra of nanosheet dispersions showed both peak position and spectral shape to vary with nanosheet thickness in a manner consistent with theoretical calculations. This allows the development of empirical metrics to extract the mean thickness of liquid dispersed nanosheets from an extinction (or absorption) spectrum. While the scattering spectra depended on nanosheet length, poor signal to noise ratios made the resultant length metric unreliable. By analyzing Raman spectra measured on graphene nanosheet networks, we found both the D/G intensity ratio and the width of the G-band to scale with mean nanosheet length allowing us to establish quantitative relationships. In addition, we elucidate the variation of 2D/G band intensities and 2D-band shape with the mean nanosheet thickness, allowing us to establish quantitative metrics for mean nanosheet thickness from Raman spectra.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...