A regular “signal attenuation” electrochemical aptasensor for highly sensitive detection of streptomycin
Abstract
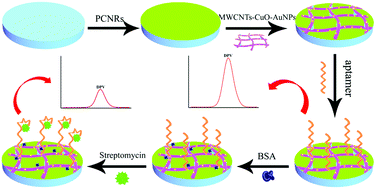
In this paper, a convenient electrochemical aptasensor for sensitive and selective determination of streptomycin antibiotic was constructed. Signal amplification strategy of the aptasensor was achieved by utilizing porous carbon nanorods, gold nanoparticles and copper oxide functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube composites as biosensing substrates. Porous carbon nanorods were adopted in our strategy as the core conductive material for signal amplification. The multiwalled carbon nanotube–copper oxide–gold nanoparticle nanocomposites combined the advantages of their components, which not only promote electron transfer, but also provide abundant binding sites for the immobilization of biomolecules. The streptomycin aptamer was immobilized on the nanocomposites' surface via the strong bonding interaction between the gold nanoparticles and the thiol group to generate a referenced differential pulse voltammetry signal, Iaptamer. Then, the streptomycin was immobilized on the aptasensor via the specific interaction between the aptamer and streptomycin to generate the attenuated signal, Istreptomycin. Under the optimized conditions, the changes in the signals were linear with the concentration of streptomycin in the range of 0.05–300 ng mL−1 with a low detection limit of 0.036 ng mL−1 when “ΔI = Iaptamer − Istreptomycin was used as the response signal for quantitative determination of streptomycin. In addition, the electrochemical aptasensor was also successfully applied to the determination of streptomycin in milk and honey samples. This highly sensitive electrochemical aptasensor is of great practical importance in food safety and could be widely extended to the detection of other antibiotics by replacing the sequence of the aptamer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...