Ultraviolet irradiation-mediated formation of Aβ42 oligomers and reactive oxygen species in Zn2+-bound Aβ42 aggregates irrespective of the removal of Zn2+†
Abstract
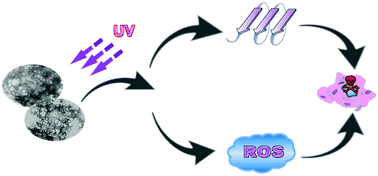
The light regulation of the aggregation and disaggregation of metal-bound Aβ peptides remains to be explored. Binding of Zn2+ to Aβ peptides is sufficient to trigger the formation of Aβ aggregates. Chelator FC-11 has a high affinity to Zn2+ and forms a 1 : 1 complex with Zn2+. Although FC-11 can effectively remove the Zn2+ ions loaded in the Aβ42 aggregates by chelation, the Zn2+ chelation cannot lead to the dissociation of the aggregates. However, controlled UV light exposure was observed to induce the dissociation of Zn2+-bound Aβ42 aggregates into sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-resistant soluble oligomers, and this dissociation does not depend on the removal of Zn2+ from the aggregates. Moreover, the UV light exposure triggers the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) including H2O2, leading to secondary structural changes in the Aβ42 aggregates. The oxidation and secondary structural changes of the aggregated Aβ42 peptides with Zn2+ should contribute to the conversion of the aggregates into soluble oligomers. The formation of ROS and oligomers can result in enhanced cytotoxicity of the aggregates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...