Enzyme free detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) using ferrocene carboxylic acid labeled monoclonal antibodies: an electrochemical approach†
Abstract
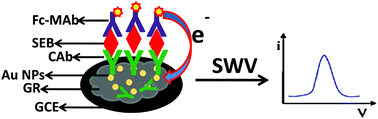
Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) is one of the most potent toxin threats in bioterrorism and can be produced as an offensive biological warfare (BW) agent (Type B). This article reports on an electrochemical detection of SEB. In order to study the detection performance, a composite containing graphene–chitosan–gold nanoparticles–capturing antibodies (GR–Ch–AuNPs–CAb) was used to modify a glassy carbon electrode (GCE). Similarly, a multi-walled carbon nanotubes–chitosan–gold nanoparticles–capturing antibody (MWCNTs–Ch–AuNPs–CAb) composite was used for comparison. Further, this bionanocomposite film modified GCE was subjected to SEB, which is detected in an electrochemical sandwich immunoassay format using ferrocene labeled-mice anti-SEB IgG (Fc–MAb) as the detection antibodies and we compared the sensitivity. The limit of detection is found to be 5 ng mL−1 and 10 ng mL−1 for GR–Ch–AuNPs and MWCNTs–Ch–Au NPs modified bionanocomposite films, respectively, and the total analysis time was 35 min. The signal amplification strategy proposed here is quite promising and can be extended for the monitoring of other biorecognition events. In addition, this is a reagentless and non-enzymatic method of electrochemical detection and is suitable for field use.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...