In vitro cell cytotoxicity profile and morphological response to polyoxometalate-stabilised gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
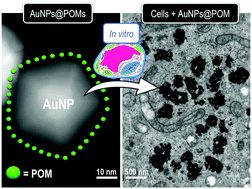
The size and redox properties of molecular polyoxometalates (POMs) make them extremely relevant for bioapplications: from disrupting tumour growth and enzyme inhibition, to DNA-intercalating agents and antimicrobial applications. Their unique ability to reversibly dominate and receive electrons, coupled with their high anionic charge, also makes them suitable for the preparation of zero-valent state metal nanoparticles (NPs) from molecular precursors. Polyoxometalate-stabilised nanoparticles (NPs@POM) are therefore an ideal delivery vehicle for bioactive POMs. Here we show how POM-stabilised gold NPs (AuNPs@POM) are massively internalised into Vero (kidney epithelial) and B16 (skin melanoma) cell lines with variable cytotoxic effects. Cell viability assays and quantification of cytoplasmic membrane composition revealed that the Vero cell line was unaltered by the internalisation of these hybrid particles; while their internalisation in B16 tumour cells produced mild cytotoxic effects and an antiproliferative cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 and G2/M phases. The observed perturbation of the tumour cell line combined with the high degree of internalisation means that these (or similar) NPs@POM could serve as candidates for a range of bioapplications in diagnostics or therapy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emergent Polyoxometalates and Soft-oxometalates

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...