Relative apoptotic potential and specific G1 arrest of stigmasterol and cinnamic acid isolated from the brown algae Padina gymnospora in HeLa and A549 cells†
Abstract
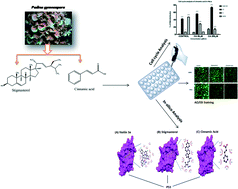
This study aimed to isolate, chemically characterize and determine the apoptotic potential of small molecules from the methanol extract of the marine brown algae Padina gymnospora collected from the Mandapam coast. The data obtained showed that a) by FT-NMR spectral results and comparison with the SDBS database, compound 1 was identified to be stigmasterol (SS) and compound 2 was identified as cinnamic acid (CA). b) The growth inhibitory activities in terms of IC50 value of SS treated A549 and HeLa cells are 10.36 μM and 12.21 μM, respectively, and those of CA are 50.18 μM and 24.81 μM, respectively at 24 h. c) The influence of SS and CA induced apoptosis was morphologically confirmed using a fluorescence microscope by AO/EB dual staining. d) The cell cycle analysis clearly demonstrates that CA treated HeLa cell growth was significantly arrested at the G1 phase. In the case of A549 cells, CA did not show any significant growth arrest. CA induced an accumulation of cells in G1 phase at the highest concentration, suggesting a block in the transition from G1 to S phase. e) Results from docking studies suggest that SS and CA bind the p53-binding pocket of MDM2, thereby displacing p53, which in turn sensitizes cancer cells to these anticancer agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...