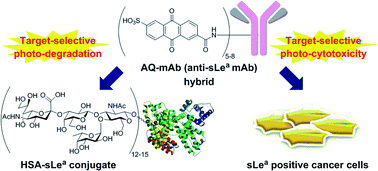
Target-selective photo-degradation of a sialyl Lewis a (sLea) conjugate and photo-cytotoxicity against sLea positive cancer cells using an anthraquinone-antibody hybrid†‡
Abstract
A purpose-designed anthraquinone–monoclonal antibody (anti-sialyl Lewis A (sLea) mAb) hybrid 6 selectively bound to and effectively degraded the target glycoprotein, HSA (human serum albumin)–sLea conjugate 4. Degradation was achieved using long wavelength UV light irradiation in the absence of any additives and under neutral conditions. Furthermore, the hybrid 6 exhibited selective photo-cytotoxicity against the sLea positive cancer cells A431 and WiDr cells only upon photo-irradiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...