Discovery of 4,6-disubstituted pyrimidines as potent inhibitors of the heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) stress pathway and CDK9†‡
Abstract
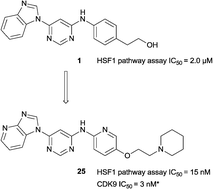
Heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) is a transcription factor that plays key roles in cancer, including providing a mechanism for cell survival under proteotoxic stress. Therefore, inhibition of the HSF1-stress pathway represents an exciting new opportunity in cancer treatment. We employed an unbiased phenotypic screen to discover inhibitors of the HSF1-stress pathway. Using this approach we identified an initial hit (1) based on a 4,6-pyrimidine scaffold (2.00 μM). Optimisation of cellular SAR led to an inhibitor with improved potency (25, 15 nM) in the HSF1 phenotypic assay. The 4,6-pyrimidine 25 was also shown to have high potency against the CDK9 enzyme (3 nM).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...