Analysis of the quantitative structure–activity relationship of glutathione-derived peptides based on different free radical scavenging systems†‡
Abstract
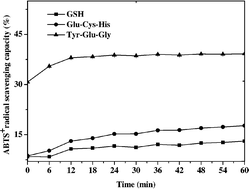
In the present study, eleven glutathione-derived peptides, including Glu-Cys-His, Pro-Leu-Gly, Pro-Cys-Gly, Phe-Lys-Leu, Leu-His-Gly, Lys-Leu-Glu, Lys-Val-His, Tyr-Glu-Gly, Tyr-His-Leu, Gly-Glu-Leu and Gly-Pro-Glu, were designed. The antioxidant activity of these peptides was investigated by single-electron-transfer (SET) reaction based assays (DPPH radical scavenging ability and reducing power), hydrogen-atom-transfer (HAT) reaction based assays (linoleic autoxidation inhibition activity, ORAC and TEAC) and hydroxyl radical scavenging activity assay. The relationship between the chemical structure and antioxidant activities of the synthetic peptides was analyzed by quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) modeling. Results showed that the amino acids next to C-terminal regions played a much more pivotal role in having high antioxidant activity than those in N-terminal regions. Besides, the difference in free radical category as well as solvent system applied in the antioxidant assay methods could result in different conclusions on the relationship between physicochemical properties (hydrophobicity, steric property and electronic property) and antioxidant activity. The amino acid with high hydrophobic property and steric property in the N-terminal also contributed to the high antioxidant activity of the glutathione-derived peptides.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...