Development of a competitive binding assay for the Burkholderia cenocepacia lectin BC2L-A and structure activity relationship of natural and synthetic inhibitors†‡
Abstract
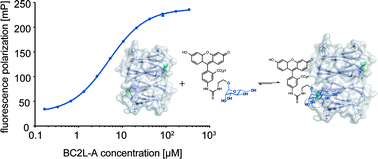
Burkholderia cenocepacia is an opportunistic Gram-negative pathogen and especially hazardous for cystic fibrosis patients. In analogy to its relative Pseudomonas aeruginosa, B. cenocepacia possess numerous lectins with roles in adhesion and biofilm formation. The LecB homolog BC2L-A is important for biofilm structure and morphology. Inhibitors of this D-mannose specific C-type lectin could be useful as tools in B. cenocepacia biofilm research and potentially as anti-biofilm compounds against chronic infections. Here, we report the development of a fluorescence polarization-based competitive binding assay and its application in an extensive structure–activity relationship study of inhibitors of BC2L-A. In contrast to its homolog LecB, BC2L-A is highly selective for D-mannose-based ligands with an absolute requirement of its hydroxyl group at C6. A strict diastereoselectivity was observed for (6S)-mannoheptose-derived ligands. Intriguingly, bioisosteric substitution or methylation of hydroxyl groups directly involved in the calcium-coordination resulted in loss of inhibition for the two homologous lectins BC2L-A and LecB.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...