Phenotypic changes associated with the fitness cost in antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli strains†
Abstract
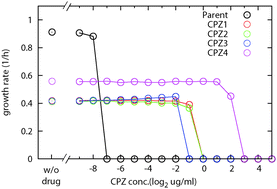
Background: the acquisition of antibiotic resistance in bacterial cells is often accompanied with a reduction of fitness in the absence of antibiotics, known as the “fitness cost”. The magnitude of this fitness cost is an important biological parameter that influences the degree to which antibiotic resistant strains become widespread. However, the relationship between the fitness cost and comprehensive phenotypic and genotypic changes remains unclear. Here, we quantified the fitness cost of resistant strains obtained by experimental evolution in the presence of various antibiotics, and analyzed how the cost correlated to phenotypic and genotypic changes in the resistant strains. Results: we measured the specific growth rate of the resistant strains in the presence of various concentrations of drugs or in their absence. In the absence of drugs, the resistant strains showed reductions of approximately 20% to 50% in growth rate compared with the parent strain, which corresponded to the fitness cost. We found that the decrease of the specific growth rate was correlated with overall expression changes between the parent and resistant strains, measured by the Euclid distance between expression profiles. We also found that there are a number of genes whose changes in expression levels were significantly correlated with the growth rate, which may account for the observed correlation between the fitness cost and overall expression changes. Conclusions: our analysis provides a basis for quantitative understanding of the mechanism of the fitness cost. This understanding may provide clues on how to influence the fitness cost that accompanies resistance acquisition and consequently how to limit the spread of antibiotic resistant strains.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...