On-chip microtubule gliding assay for parallel measurement of tau protein species†
Abstract
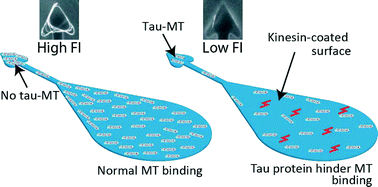
Tau protein is a well-established biomarker for a group of neurodegenerative diseases collectively called tauopathies. So far, clinically relevant detection of tau species in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cannot be achieved without immunological methods. Recently, it was shown that different tau isoforms including the ones carrying various types of mutations affect microtubule (MT)–kinesin binding and velocity in an isoform specific manner. Here, based on these observations, we developed a microfluidic device to analyze tau mutations, isoforms and their ratios. The assay device consists of three regions: a MT reservoir which captures MTs from a solution to a kinesin-coated surface, a microchannel which guides gliding MTs, and an arrowhead-shaped collector which concentrates MTs. Tau-bound fluorescently labeled MTs (tau-MTs) were assayed, and the increase in fluorescence intensity (FI) corresponding to the total number of MTs accumulated was measured at the collector. We show that our device is capable of differentiating 3R and 4R tau isoform ratios and effects of point mutations within 5 minutes. Furthermore, radially oriented collector regions enable simultaneous FI measurements for six independent assays. Performing parallel assays in the proposed device with minimal image processing provides a cost-efficient, easy-to-use and fast tau detection platform.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Lab on a Chip Recent Open Access Articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...