High biomass loadings of 40 wt% for efficient fractionation in biorefineries with an aqueous solvent system without adding adscititious catalyst†
Abstract
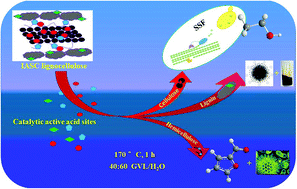
Development of lignocellulosic biorefineries requires improved environmental and cost-effective processes in addition to tailoring the lignocellulosic constitutions with the desired biofuels and chemicals. Here, we first report a novel strategy of lignocellulose fractionation at solid biomass loadings up to 40 wt% through irradiation assisted self-catalysis (IASC) with a green solvent aqueous system consisting of 40 wt% γ-valerolactone and 60 wt% water (40 : 60 GVL/H2O) with no adscititious catalyst. Each fraction of cellulose, hemicellulsoe and lignin can be prone to upgrade to desired biofuels and bioproducts. The irradiation-mediated carboxyl, aldehyde, and phenol groups in biomass act as weak active acid sites for (hemi) cellulose cleavage in 40 : 60 GVL/H2O and their subsequent self-catalyzed hydrolysis to soluble carbohydrates and their derived products, which are catalytically upgraded to furans with an 80% conversion rate, and/or fermentative upgrading to microbial oils (biomass 31 g L−1 and lipid content 36.5 wt%). The regenerated cellulose can achieve approximately 184.3 g L−1 monomeric glucose (total concentration of soluble C5 and C6 sugars is 231 g L−1) and high potential ethanol titers of 88.5 g L−1 during SSF fermentation. The obtained lignin also showed good reactivity for valorization to nanoparticle functional materials and/or low molecular aromatics. In the end, the overall process mass balance at the laboratory-scale level was preliminarily evaluated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...