Iron-catalyzed carbonylation of aryl halides with arylborons using stoichiometric chloroform as the carbon monoxide source†
Abstract
A general iron-catalyzed carbonylative Suzuki–Miyaura coupling of aryl halides with arylborons is reported, using stoichiometric CHCl3 as the CO source. The high efficiency, economy, selectivity, and operational simplicity of this transformation make this method a valuable tool in organic synthesis. Importantly, the presented strategy allows effective 13C labeling simply by using the commercially available 13C-labeled CHCl3. On the basis of the initial mechanistic exploration, an aryl radical intermediate is proposed in the present carbonylation process.
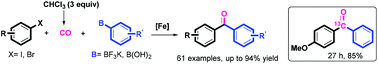


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...