Autohydrolysis pretreatment of softwood – enhancement by phenolic additives and the effects of other compounds†
Abstract
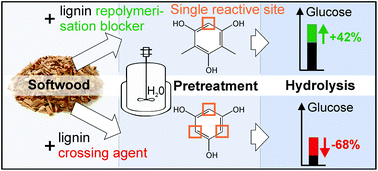
The effects of different additives on lignin repolymerisation in the autohydrolysis pretreatment of softwood and the consequences for enzymatic cellulose digestibility have been studied. The study comprised 35 substances including alcohols, amines, heterocyclic and other compounds. It has been shown that lignin repolymerisation does not only hinder hydrolysis by the deactivation of cellulases, but can also obstruct their access to cellulose. A new class of phenolic additives has been discovered that can block lignin repolymerisation and thus increase glucose yields in hydrolysis by more than 40%. Dimethylphloroglucinol was found to be even more effective than 2-naphthol, the most effective lignin repolymerisation blocker reported to date. The study reveals that effective additives have to be highly nucleophilic and must not act as a crossing agent for lignin fragments, which can dramatically worsen glucose yields. Phenolic compounds activated by several hydroxy groups with only a single reactive aromatic site are however very beneficial in enhancing pretreatment. The order of effectiveness of the tested compounds is consistent with the hypothesis that they compete with the aromatic rings present in lignin for lignin carbocations. These ions have been proposed earlier to be intermediates in the formation of repolymerised lignin structures. While compounds activated towards electrophilic substitution generally had a high impact, compounds that can stop radical repolymerisation had no effect. The gained insights open up the possibility to identify numerous further additives that can enhance autohydrolysis, steam and acidic pretreatments of lignocellulose.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...