Catalytic oxidation of cellulose to formic acid in H5PV2Mo10O40 + H2SO4 aqueous solution with molecular oxygen†
Abstract
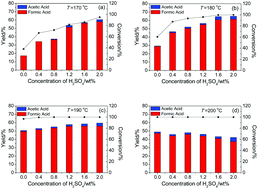
The preparation of formic acid (FA) by catalytic oxidation of sustainable biomass is of significant conceptual and practical interest, because FA is an important chemical and is now produced from non-sustainable fossil fuel. In this work, we found that a binary catalyst of Keggin-type heteropoly acid H5PV2Mo10O40 + H2SO4 was efficient in oxidizing biomass cellulose to FA using oxygen as an oxidant in aqueous solution. In the oxidation, the pH of the aqueous solutions plays a key role, and a decrease in pH improves the transformation. Cellulose was transformed to FA with conversions from 60% to 100% and FA yields from 28% to 61% (based on the carbon atoms in the feedstock) after 5 min of reaction at 180 °C, using H2SO4 as an additive to decrease the pH from 1.79 to 0.56. The influences of the pH on both the catalyst and the reaction pathway were discussed. By decreasing the pH, the oxidation potential and electron affinity were increased due to the formation of protonated H5PV2Mo10O40 and VO2+ species, favoring the reduction of the catalyst and oxidation of the substrate. A reaction pathway for the generation of products was proposed, and the influence of the pH on the reaction pathway was also discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...