Effect of Bactrocera oleae on phenolic compounds and antioxidant and antibacterial activities of two Algerian olive cultivars
Abstract
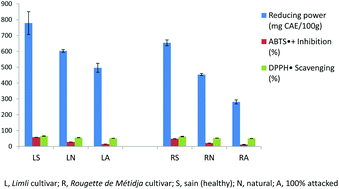
Bactrocera oleae, an olive fruit fly, is a major olive pest in Algeria. In this study, olives of two Algerian cultivars (Limli and Rougette de Métidja) with different degrees of infestation by the Bactrocera oleae fly (0%, not attacked; 100%, all attacked; and real %) were analysed. The influence of this pest on individual phenolic compounds (HPLC–DAD–FLD) and antioxidant profiles was ascertained. The antibacterial activity against 8 human enteropathogenic bacteria was also assessed. The results show that Rougette de Métidja, the cultivar with higher drupe size, was attacked to a greater degree than Limli, and the B. oleae attack caused a significant decrease in the total phenolic contents (>50%), including oleuropein, verbascoside, luteolin-7-O-glucoside, tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol. The antioxidant and antibacterial activities were highly correlated with the phenolic levels. Extracts from healthy olives were more effective against bacteria than those obtained from attacked olives. Globally, olive fly affected significantly the phenolic compounds of olives and their biological properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...