Polydatin attenuates d-galactose-induced liver and brain damage through its anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in mice
Abstract
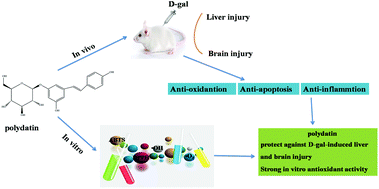
Accumulating evidence has shown that chronic injection of D-galactose (D-gal) can mimic natural aging, with accompanying liver and brain injury. Oxidative stress and apoptosis play a vital role in the aging process. In this study, the antioxidant ability of polydatin (PD) was investigated using four established in vitro systems. An in vivo study was also conducted to investigate the possible protective effect of PD on D-gal-induced liver and brain damage. The results showed that PD had remarkable in vitro free radical scavenging activity on 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH˙), 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzo-thiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS+˙) radical ions, and hydroxyl and superoxide anions. Results in vivo indicated that, in a group treated with D-gal plus PD, PD remarkably decreased the depression of body weight and organ indexes, reduced the levels of the serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alleviated alterations in liver and brain histopathology. PD also significantly decreased the level of MDA and elevated SOD, GSH-Px, CAT activity and T-AOC levels in the liver and brain. In addition, the levels of inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in serum were markedly reduced after PD treatment. Western blotting results revealed that PD treatment noticeably attenuated the D-gal-induced elevation of Bcl-2/Bax ratio and caspase-3 protein expression in liver and brain. Overall, our findings indicate that PD treatment could effectively attenuate D-gal-induced liver and brain damage, and the mechanism might be associated with decreasing the oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis caused by D-gal. PD holds good potential for further development into a promising pharmaceutical candidate for the treatment of age-associated diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...